MAP OF GERMANY
 MAP OF GERMANY
MAP OF GERMANY
Here you will find Maps of Germany and maps of cities throughout Europe. The 100 largest cities here are listed by population. Some of the most visited cities in Germany are of course Berlin, Hamburg and of course Flensburg. Each city links to a map of the city in Germany. You can read about most cities via the link on each city.
How far is it to a city in Germany?
We have chosen to tell you how far it is from the border at both Padborg and Puttgarden to the individual towns. You can see it by clicking on the link on each city.
MAP OF ALL CITIES IN GERMANY
East and West Germany
 MAP OF GERMANY, GERMANY MAP
MAP OF GERMANY, GERMANY MAP
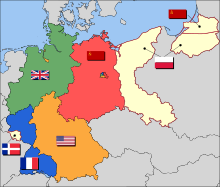
American, Soviet, British, and French occupation zones in Germany and the French-controlled Saar Protectorate, 1947. Territories east of the Oder-Neisse line were transferred to Poland and the Soviet Union under the terms of the Potsdam Conference.[86]
After Nazi Germany surrendered, the Allies partitioned Berlin and Germany’s remaining territory into four occupation zones. The western sectors, controlled by France, the United Kingdom, and the United States, were merged on 23 May 1949 to form the Federal Republic of Germany (German: Bundesrepublik Deutschland); on 7 October 1949, the Soviet Zone became the German Democratic Republic (German: Deutsche Demokratische Republik; DDR). They were informally known as West Germany and East Germany.[87] East Germany selected East Berlin as its capital, while West Germany chose Bonn as a provisional capital, to emphasise its stance that the two-state solution was temporary.[88]
West Germany was established as a federal parliamentary republic with a “social market economy“. Starting in 1948 West Germany became a major recipient of reconstruction aid under the Marshall Plan.[89] Konrad Adenauer was elected the first Federal Chancellor of Germany in 1949. The country enjoyed prolonged economic growth (Wirtschaftswunder) beginning in the early 1950s.[90] West Germany joined NATO in 1955 and was a founding member of the European Economic Community.[91]
East Germany was an Eastern Bloc state under political and military control by the USSR via occupation forces and the Warsaw Pact. Although East Germany claimed to be a democracy, political power was exercised solely by leading members (Politbüro) of the communist-controlled Socialist Unity Party of Germany, supported by the Stasi, an immense secret service.[92] While East German propaganda was based on the benefits of the GDR’s social programmes and the alleged threat of a West German invasion, many of its citizens looked to the West for freedom and prosperity.[93] The Berlin Wall, built in 1961, prevented East German citizens from escaping to West Germany, becoming a symbol of the Cold War.[94]
Tensions between East and West Germany were reduced in the late 1960s by Chancellor Willy Brandt‘s Ostpolitik.[95] In 1989, Hungary decided to dismantle the Iron Curtain and open its border with Austria, causing the emigration of thousands of East Germans to West Germany via Hungary and Austria. This had devastating effects on the GDR, where regular mass demonstrations received increasing support. In an effort to help retain East Germany as a state, the East German authorities eased border restrictions, but this actually led to an acceleration of the Wende reform process culminating in the Two Plus Four Treaty under which Germany regained full sovereignty. This permitted German reunification on 3 October 1990, with the accession of the five re-established states of the former GDR.[96] The fall of the Wall in 1989 became a symbol of the Fall of Communism, the Dissolution of the Soviet Union, German Reunification and Die Wende.[97]
Reunified Germany and the European Union

The Berlin Wall during its fall in 1989, with the Brandenburg Gate in the background
United Germany was considered the enlarged continuation of West Germany so it retained its memberships in international organisations.[98] Based on the Berlin/Bonn Act (1994), Berlin again became the capital of Germany, while Bonn obtained the unique status of a Bundesstadt (federal city) retaining some federal ministries.[99] The relocation of the government was completed in 1999, and modernisation of the east German economy was scheduled to last until 2019.[100][101]
Since reunification, Germany has taken a more active role in the European Union, signing the Maastricht Treaty in 1992 and the Lisbon Treaty in 2007,[102] and co-founding the Eurozone.[103] Germany sent a peacekeeping force to secure stability in the Balkans and sent German troops to Afghanistan as part of a NATO effort to provide security in that country after the ousting of the Taliban.[104][105]
In the 2005 elections, Angela Merkel became the first female chancellor. In 2009 the German government approved a €50 billion stimulus plan.[106] Among the major German political projects of the early 21st century are the advancement of European integration, the energy transition (Energiewende) for a sustainable energy supply, the “Debt Brake” for balanced budgets, measures to increase the fertility rate (pronatalism), and high-tech strategies for the transition of the German economy, summarised as Industry 4.0.[107] During the 2015 European migrant crisis, the country took in over a million refugees and migrants.[108]
Geography
Germany is the seventh-largest country in Europe;[4] bordering Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria to the southeast, and Switzerland to the south-southwest. France, Luxembourg and Belgium are situated to the west, with the Netherlands to the northwest. Germany is also bordered by the North Sea and, at the north-northeast, by the Baltic Sea. German territory covers 357,022 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 348,672 km2 (134,623 sq mi) of land and 8,350 km2 (3,224 sq mi) of water.
Elevation ranges from the mountains of the Alps (highest point: the Zugspitze at 2,963 metres or 9,721 feet) in the south to the shores of the North Sea (Nordsee) in the northwest and the Baltic Sea (Ostsee) in the northeast. The forested uplands of central Germany and the lowlands of northern Germany (lowest point: in the municipality Neuendorf-Sachsenbande, Wilstermarsch at 3.54 metres or 11.6 feet below sea level[109]) are traversed by such major rivers as the Rhine, Danube and Elbe. Significant natural resources include iron ore, coal, potash, timber, lignite, uranium, copper, natural gas, salt, and nickel.[4]
Constituent states
Germany is a federation and comprises sixteen constituent states which are collectively referred to as Länder.[131] Each state (Land) has its own constitution,[132] and is largely autonomous in regard to its internal organisation.[131] As of 2017 Germany is divided into 401 districts (Kreise) at a municipal level; these consist of 294 rural districts and 107 urban districts.[133]
Most of Germany has a temperate climate, ranging from oceanic in the north to continental in the east and southeast. Winters range from the cold in the Southern Alps to cool and are generally overcast with limited precipitation, while summers can vary from hot and dry to cool and rainy. The northern regions have prevailing westerly winds that bring in moist air from the North Sea, moderating the temperature and increasing precipitation. Conversely, the southeast regions have more extreme temperatures.[110]
From February 2019–2020, average monthly temperatures in Germany ranged from a low of 3.3 °C (37.9 °F) in January 2020 to a high of 19.8 °C (67.6 °F) in June 2019.[111] Average monthly precipitation ranged from 30 litres per square metre in February and April 2019 to 125 litres per square metre in February 2020.[112] Average monthly hours of sunshine ranged from 45 in November 2019 to 300 in June 2019. The highest temperature ever recorded in Germany was 42.6 °C on 25 July 2019 in Lingen and the lowest was −37.8 °C on 12 February 1929 in Wolnzach.
| Berlin | 3,426,354 |
| Hamborg | 1,739,117 |
| München | 1,260,391 |
| Köln | 963,395 |
| Frankfurt am Main | 650,000 |
| Essen | 593,085 |
| Stuttgart | 589,793 |
| Dortmund | 588,462 |
| Düsseldorf | 573,057 |
| Bremen | 546,501 |
| Hannover | 515,140 |
| Leipzig | 504,971 |
| Duisburg | 504,358 |
| Nürnberg | 499,237 |
| Dresden | 486,854 |
| Wandsbek | 411,422 |
| Bochum | 385,729 |
| Bochum-Hordel | 380,000 |
| Wuppertal | 360,797 |
| Bielefeld | 331,906 |
| Bonn | 313,125 |
| Mannheim | 307,960 |
| Marienthal | 287,101 |
| Karlsruhe | 283,799 |
| Hamburg-Nord | 280,000 |
| Wiesbaden | 272,432 |
| Münster | 270,184 |
| Gelsenkirchen | 270,028 |
| Aachen | 265,208 |
| Mönchengladbach | 261,742 |
| Augsburg | 259,196 |
| Eimsbüttel | 251,907 |
| Altona | 250,192 |
| Chemnitz | 247,220 |
| Braunschweig | 244,715 |
| Krefeld | 237,984 |
| Halle | 234,107 |
| Hamburg-Mitte | 233,144 |
| Kiel | 232,758 |
| Magdeburg | 229,826 |
| Neue Neustadt | 226,851 |
| Oberhausen | 219,176 |
| Freiburg im Breisgau | 215,966 |
| Lübeck | 212,207 |
| Erfurt | 203,254 |
| Harburg | 202,571 |
| Hagen | 198,972 |
| Rostock | 198,293 |
| Kassel | 194,501 |
| Hamm | 185,327 |
| Mainz | 184,997 |
| Saarbrücken | 181,227 |
| Herne | 172,108 |
| Mülheim | 171,000 |
| Neukölln | 167,248 |
| Osnabrück | 166,462 |
| Solingen | 164,359 |
| Ludwigshafen am Rhein | 163,196 |
| Leverkusen | 162,738 |
| Oldenburg | 159,218 |
| Neuss | 152,457 |
| Prenzlauer Berg | 148,878 |
| Kreuzberg | 147,532 |
| Potsdam | 145,292 |
| Heidelberg | 143,345 |
| Paderborn | 142,161 |
| Darmstadt | 140,385 |
| Würzburg | 133,731 |
| Regensburg | 129,151 |
| Wolfsburg | 123,064 |
| Recklinghausen | 122,438 |
| Göttingen | 122,149 |
| Heilbronn | 120,733 |
| Ingolstadt | 120,658 |
| Ulm | 120,451 |
| Bottrop | 119,909 |
| Charlottenburg | 119,857 |
| Bergedorf | 119,665 |
| Pforzheim | 119,313 |
| Offenbach | 119,192 |
| Friedrichshain | 117,829 |
| Bremerhaven | 117,446 |
| Remscheid | 117,118 |
| Schöneberg | 115,976 |
| Nippes | 113,487 |
| Reutlingen | 112,627 |
| Fürth | 112,025 |
| Moers | 107,816 |
| Koblenz | 107,319 |
| Siegen | 107,242 |
| Bergisch Gladbach | 106,184 |
| Jena | 104,712 |
| Gera | 104,659 |
| Marzahn | 103,768 |
| Hildesheim | 103,052 |
| Erlangen | 102,675 |
| Witten | 101,247 |
| Salzgitter | 101,079 |
| Trier | 100,129 |
| Zwickau | 98,796 |